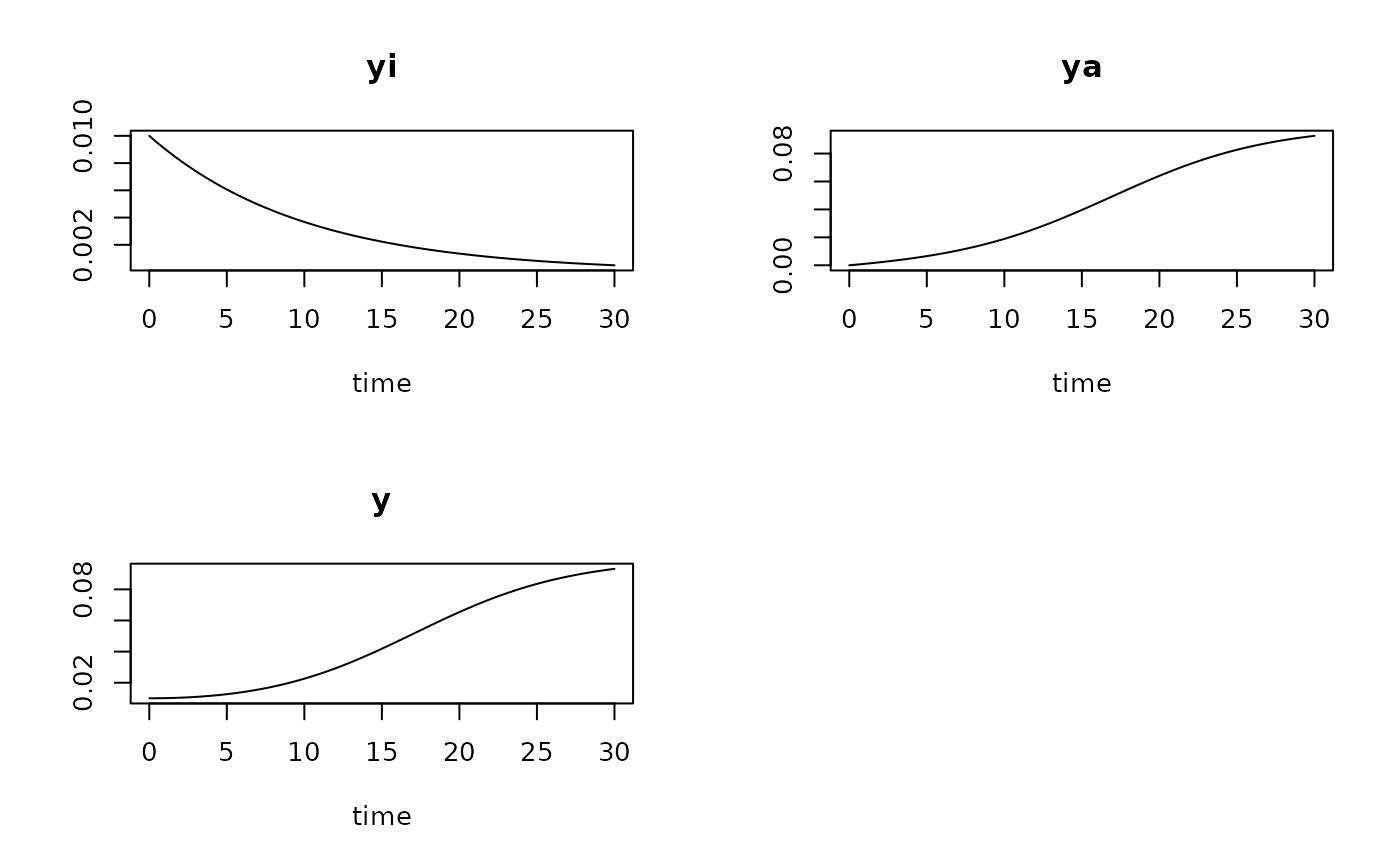
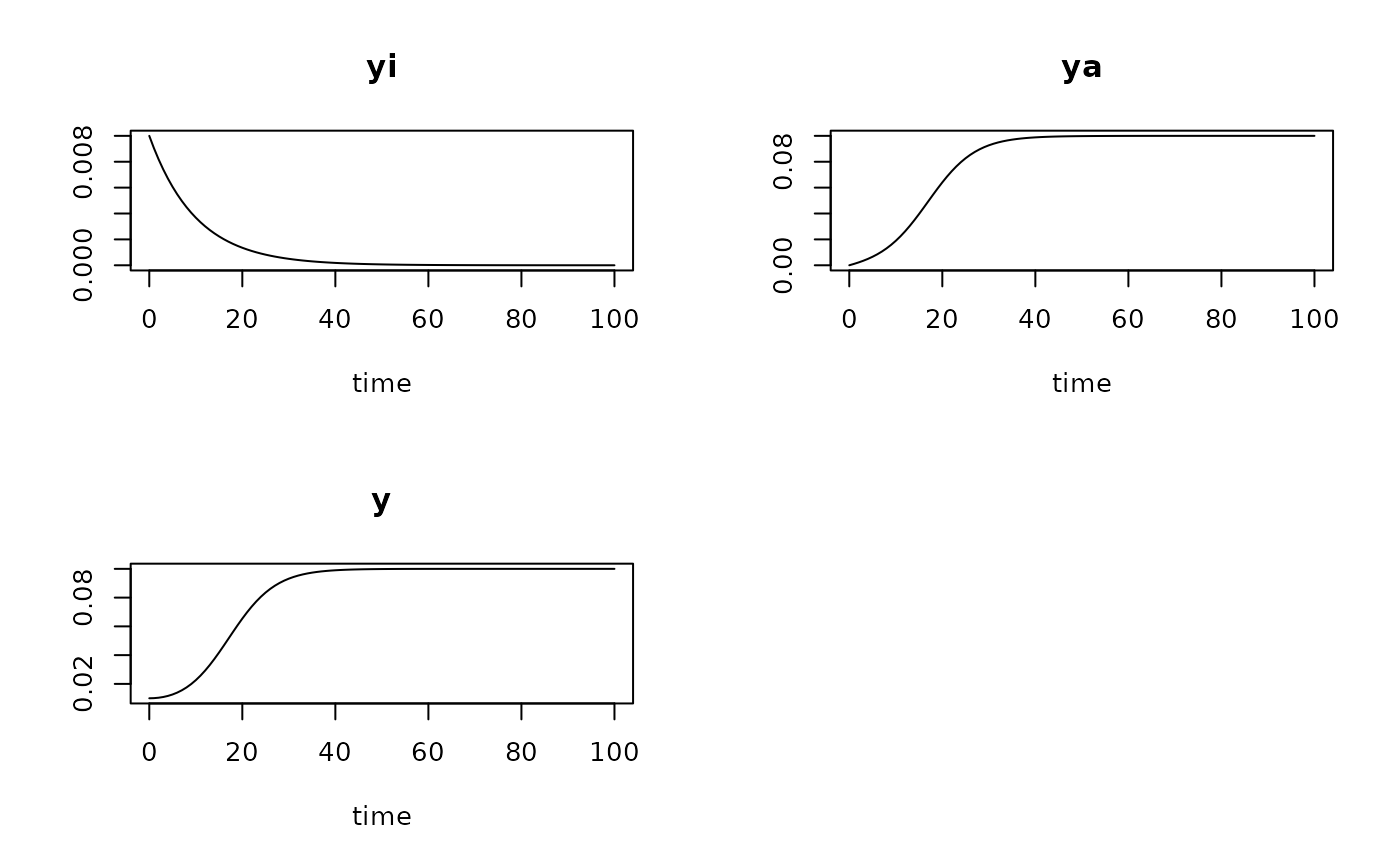
System of two differential equations describing bacterial growth as two-step process of activation (or adaptation) and growth.
Arguments
- time
actual time (for the ode) resp. vector of simulation time steps.
- y
named vector with state of the system (yi, ya: abundance of inactive and active organisms, e.g. concentration of inactive resp. active cells).
- parms
parameters of the two-step growth model:
yi, yainitial abundance of active and inactive organisms,kwactivation (“wakeup”) constant (1/time),mumaxmaximum growth rate (1/time),Kcarrying capacity (max. abundance).
- ...
placeholder for additional parameters (for user-extended versions of this function)
Value
For ode_twostep: matrix containing the simulation outputs.
The return value of has also class deSolve.
For grow_twostep: vector of dependent variable (y):
timetime of the simulationyiconcentration of inactive cellsyaconcentration of active cellsytotal cell concentration
Details
The model is given as a system of two differential equations:
$$dy_i/dt = -kw * yi$$ $$dy_a/dt = kw * yi + mumax * (1 - (yi + ya)/K) * ya$$
that are then numerically integrated ('simulated') according to time (t). The model assumes that the population consists of active (\(y_a\)) and inactive (\(y_i\)) cells so that the observed abundance is (\(y = y_i + y_a\)). Adapting inactive cells change to the active state with a first order 'wakeup' rate (\(kw\)).
Function ode_twostep is the system of differential equations,
whereas grow_twostep runs a numerical simulation over time.
A similar two-compartment model, but without the logistic term, was discussed by Baranyi (1998).
References
Baranyi, J. (1998). Comparison of stochastic and deterministic concepts of bacterial lag. J. heor. Biol. 192, 403–408.
See also
Other growth models:
grow_baranyi(),
grow_exponential(),
grow_gompertz(),
grow_gompertz2(),
grow_huang(),
grow_logistic(),
grow_richards(),
growthmodel,
ode_genlogistic()
Other growth models:
grow_baranyi(),
grow_exponential(),
grow_gompertz(),
grow_gompertz2(),
grow_huang(),
grow_logistic(),
grow_richards(),
growthmodel,
ode_genlogistic()